BY PRISCA OGBO
WORLD Diabetes Day (WDD) is observed annually on November 14, serving as the largest global awareness campaign dedicated to diabetes. Established in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the World Health Organization (WHO), the day aims to address the growing health threat posed by diabetes, a condition affecting millions worldwide. The date was chosen in honor of Sir Frederick Banting, who co-discovered insulin in 1921, a breakthrough that revolutionized diabetes management.
Each year, World Diabetes Day focuses on a specific theme to raise awareness and mobilize action. Recent themes have emphasized the importance of access to diabetes care, reflecting the global disparities in healthcare accessibility. The campaign underscores the need for equitable resources, treatment, and education for people living with diabetes, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
Diabetes is one of the most pressing public health issues, with over 537 million adults (20–79 years) currently living with the disease, according to the IDF. This number is expected to rise to 643 million by 2030 if urgent measures are not taken. The condition is categorized into two main types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition requiring daily insulin injections.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A largely preventable form, often linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity.
Objectives of World Diabetes Day
The key objectives of WDD include:
- Raising Awareness: Educating the public about diabetes prevention, early detection, and effective management.
- Advocacy: Urging policymakers to prioritize diabetes care in national health agendas.
- Promoting Healthy Lifestyles: Encouraging individuals to adopt habits that reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
- Empowering Communities: Providing tools and resources for individuals and healthcare providers to combat the disease effectively.
Activities and Campaigns
World Diabetes Day is marked by various activities worldwide, including:
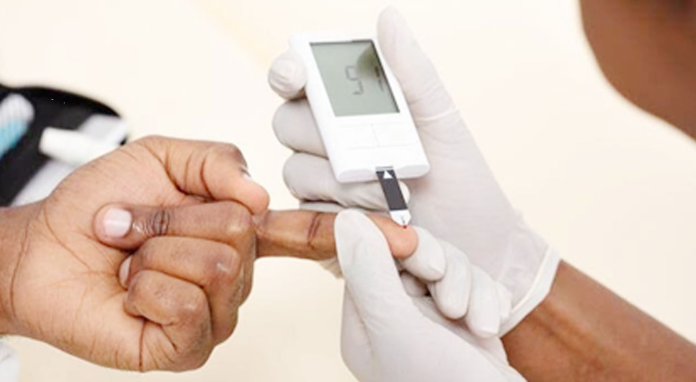
– Free Screening Campaigns: Offering blood glucose tests to identify undiagnosed cases.
– Educational Workshops: Providing information on healthy diets, physical activity, and diabetes management.
– Advocacy Events: Encouraging governments and organizations to commit resources toward diabetes care.
The Importance of Access to Diabetes Care
One of the central messages of WDD is the need for affordable and accessible diabetes care. Millions of people, particularly in underprivileged regions, lack access to essential medications like insulin, diagnostic tools, and proper medical guidance. Bridging this gap is crucial to reducing the disease’s impact on global health.
World Diabetes Day serves as a vital reminder of the collective responsibility to combat diabetes. By fostering awareness, advocating for policy changes, and promoting healthy lifestyles, we can work toward a future where everyone, regardless of location or income, has access to the care they need.
Detecting Diabetes Early
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for preventing complications and managing the condition effectively. Diabetes, particularly Type 2, often develops gradually and may go unnoticed for years.
Early detection involves staying vigilant about symptoms and regularly consulting healthcare providers if you’re at risk. With prompt intervention, you can effectively manage or even prevent diabetes.
Recognizing Early Symptoms
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria):
High blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter and remove excess glucose, leading to frequent urination.
- Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia):
Increased urination results in dehydration, causing an intense feeling of thirst.
- Unexplained Weight Loss:
Despite eating normally or even more, the body may start breaking down fat and muscle for energy because it can’t access glucose efficiently.
- Increased Hunger (Polyphagia):
A lack of insulin or insulin resistance can cause cells to signal hunger even after eating.
- Fatigue:
Persistent tiredness may result from the body’s inability to use glucose for energy.
- Blurred Vision:
High blood sugar can affect the eyes, causing swelling in the lenses and difficulty focusing.
- Slow Healing of Wounds:
Elevated blood sugar levels can impair blood flow and affect the body’s ability to repair itself.
- Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet:
Nerve damage (neuropathy), a common early sign of diabetes, often causes these sensations.
- Darkened Skin Patches (Acanthosis Nigricans):
This condition, characterized by dark, velvety patches on the neck, armpits, or groin, can be an early indicator of insulin resistance.
Risk Factors to Consider
Even without symptoms, certain risk factors increase the likelihood of diabetes:
– Family history of diabetes.
– Obesity or being overweight.
– Sedentary lifestyle with minimal physical activity.
– Age (risk increases after 45).
– History of gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby weighing over 4 kg.
– High blood pressure, high cholesterol, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Preventive Measures for At-Risk Individuals
– Maintain a Healthy Diet:Focus on whole grains, vegetables, lean protein, and limit sugary or processed foods.
– Stay Physically Active: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
– Regular Screenings: If you have risk factors or are over 45, consider annual diabetes screenings.
– Manage Weight: Even a 5-10% weight loss can significantly reduce diabetes risk.
The Delta State “10 Million” Campaign for People with Diabetes
The recently concluded Delta State “10 Million” campaign was a bold initiative, aimed at tackling the rising prevalence of diabetes within the state, and in just 10 days, over 150,000 Deltans were screened for free. With diabetes becoming a growing public health challenge in Nigeria, this campaign underscored the state’s commitment to raising awareness, providing effective treatment, and ensuring preventive healthcare measures. By targeting improved health outcomes for individuals living with diabetes, the campaign sought to empower Deltans to lead healthier lives and reduce the socioeconomic burden of the disease.
Diabetes affects millions of Nigerians, with many cases going undiagnosed due to poor awareness and limited access to medical facilities. Delta State’s initiative aimed to bridge this gap by providing essential services to the population. The “10 Million” campaign encapsulated a twofold strategy:
- Awareness and Prevention: Creating widespread knowledge about diabetes, its causes, risk factors, and prevention strategies among all demographic groups.
- Affordable Care and Support: Screening/making diagnosis, treatment, and management of diabetes accessible and affordable for all Deltans, particularly underserved communities.
Key Components of the “10 Million” Campaign
- Extensive Awareness Programs:
– Hosting community outreach events, workshops, and seminars to educate the public about diabetes.
– Collaborating with schools and workplaces to integrate diabetes awareness into everyday discussions.
- Accessible Screening Services:
– Healthcare units deployed across the 25 local government areas of the state for free diabetes screening and testing services.
– Training local healthcare providers to perform screenings and deliver results efficiently.
- Provision of Subsidized Medications and Supplies:
– Partnering with pharmaceutical companies and organizations to supply affordable insulin, glucose monitors, and test strips.
– Ensuring a steady stock of these supplies in primary healthcare centers.
- Training Healthcare Professionals:
– Conducting specialized training programs for doctors, nurses, and community health workers in diabetes management.
– Encouraging evidence-based practices in treating and preventing diabetes-related complications.
Subsidized Healthcare in Delta State
Delta State has a reputation for being proactive in improving access to quality healthcare. Through various programs, Deltans can access affordable and subsidized healthcare services that significantly alleviate the financial burden of medical expenses. The state’s healthcare model emphasizes inclusivity, ensuring no one is left behind.
Delta State Contributory Health Commission (DSCHC):
The Delta State Contributory Health Scheme (DSCHS) has been a cornerstone of subsidized healthcare in the state. This insurance-based programme allows Delta state’s civil servants and residents to access affordable healthcare services for a nominal premium. It covers for a wide range of health services, including consultations, medications, diagnostics, and surgeries, availability of plans for individuals, families, vulnerable populations and access to accredited healthcare facilities across the state.
How to Enroll
Residents can register for the scheme by visiting DSCHC offices, accredited health centers, or online portals. Subsidized enrollment fees and flexible payment options ensure affordability.
The Delta State “10 Million” campaign for people with diabetes is a transformative initiative that reflects the state’s dedication to addressing public health challenges. Combined with its subsidized healthcare programs, the campaign has the potential to significantly improve the quality of life for millions of residents. By prioritizing accessibility, affordability, and awareness, Delta State is setting a benchmark for healthcare delivery in Nigeria, ensuring that every Deltan has the opportunity to lead a healthy and productive life.